💻 Profile Breakdown
In this section, we’ll break down the structure and functionality of a mobileconfig file. Below is an example of the mau_autoupdate_3_day.mobileconfig file, designed for Microsoft AutoUpdate (MAU) on macOS. We’ll explore its key components to understand how it works. 🔍
💻 Example File
Here’s an example of the mau_autoupdate_3_day.mobileconfig file, which configures the Microsoft AutoUpdate app to automate update checks and installation. The file contains several key settings that manage how the application handles updates.
🧩 File Breakdown
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE plist PUBLIC "-//Apple//DTD PLIST 1.0//EN" "http://www.apple.com/DTDs/PropertyList-1.0.dtd">
<plist version="1.0">
<dict>
<key>PayloadContent</key>
<array>
<dict>
<key>Applications</key>
<dict>
<key>/Library/Application Support/Microsoft/MAU2.0/Microsoft AutoUpdate.app</key>
<dict>
<key>Application ID</key>
<string>MSau04</string>
<key>LCID</key>
<integer>1033</integer>
<key>UpdateDeadline.DaysBeforeForcedQuit</key>
<integer>14</integer>
</dict>
</dict>
<key>ChannelName</key>
<string>Current</string>
<key>HowToCheck</key>
<string>AutomaticDownload</string>
<key>PayloadDisplayName</key>
<string>Microsoft AutoUpdate</string>
<key>PayloadIdentifier</key>
<string>com.microsoft.autoupdate2.14daypolicy</string>
<key>PayloadType</key>
<string>com.microsoft.autoupdate2</string>
<key>PayloadUUID</key>
<string>A1B2C3D4-14D1-14D1-14D1-1234567890AB</string>
<key>PayloadVersion</key>
<integer>1</integer>
<key>UpdateCheckFrequency</key>
<integer>360</integer>
<key>UpdateCheckInterval</key>
<integer>240</integer>
<key>UpdateDeadline.FinalCountDown</key>
<integer>60</integer>
<key>UpdateDeadline.StartAutomaticUpdates</key>
<integer>3</integer>
</dict>
</array>
</dict>
</plist>Please note that this example has been simplified for clarity. ✍️
🔑 Key Sections
For more detailed information about the Microsoft Auto Update settings, refer to the offical documentation here.📚
1. HowToCheck
Specifies the update check method. Set to AutomaticDownload, ensuring updates are both downloaded and installed automatically. Other options include AutomaticCheck. 📥
Some keys, like HowToCheck, can lock certain functions from users, such as preventing manual control over update checks and installations.
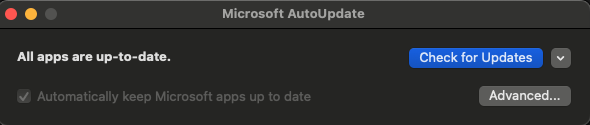
2. ChannelName
Defines the update channel. In this case, Current is used to indicate the production update channel. Other options include Beta or Preview. 📡
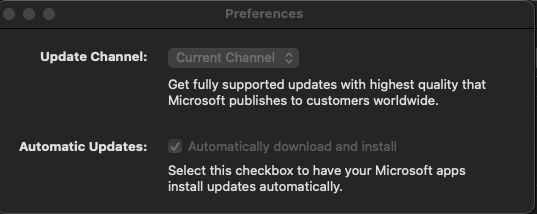
3. StartDaemonOnAppLaunch
Ensures the update daemon starts automatically when an Office app is launched. The default value is true, but it can be set to false. 🚀
4. UpdateCheckInterval
Defines how often updates are checked, in minutes. Set to 240 minutes (4 hours) here, it can be customized based on needs. ⏰
5. UpdateDeadline.StartAutomaticUpdates
Determines when automatic updates will start, in hours. Set to 3 hours before updates are initiated. 🕒
6. UpdateDeadline.FinalCountDown
The countdown time (in minutes) before a forced quit occurs. Here it is set to 60 minutes. ⏳
🛠️ Customizing Configs
Each application may have unique formatting and spacing requirements for configuration files. To simplify the process, you can use specialized tools or edit unsigned mobileconfig files directly with an advanced text editor like Visual Studio Code for quick adjustments. 📝
Alternatively, you can use the application itself to configure settings, then locate and convert the corresponding plist file into a mobileconfig for deployment.
🔄 Step-by-Step Guide:
Open the Application
Launch the application you want to configure. 💻Adjust Settings
Navigate to the preferences or settings section and make the desired changes. ⚙️Locate the Generated plist
After saving your settings, find the plist file containing the configuration you just set. Common locations include:/Library/Preferences/📂/Users/<username>/Library/Preferences/📁
Convert the plist to a mobileconfig
- Open the plist file with tools like ProfileCreator or iMazing. 🔧
- Modify additional settings, metadata, or organizational details as necessary. 🛠️
- Export the file as a mobileconfig for deployment. 📤
This approach takes advantage of the app’s native configuration options, ensuring accuracy and compatibility when pushing settings via an MDM solution. 🔄
🧰 Tools for Configs
Here are some excellent tools to help you create custom configuration profiles from scratch or fine-tune existing ones with ease:
Apple Configurator 2
A user-friendly tool for creating and managing configuration profiles. Ideal for organizations using Apple devices. 🍏ProfileCreator
A free, open-source macOS application designed specifically for building and editing configuration profiles. 🆓Visual Studio Code
A powerful code editor that can be used to edit unsigned mobileconfig files. You can open an unsigned mobileconfig file directly in Visual Studio Code, make adjustments, and save your changes. This method is especially helpful for fine-tuning configurations or fixing issues in existing files. 💻Plist Editor Pro
A specialized tool for working with property list files (.plist), which form the basis of mobileconfig files. 📂MCXToProfile
A command-line tool that converts older MCX settings into modern configuration profiles. 🖥️iMazing
A versatile tool for managing Apple devices, including creating, editing, and deploying configuration profiles. Its intuitive interface makes it easy to create custom mobileconfig files without requiring extensive technical knowledge. 📲